Clouds
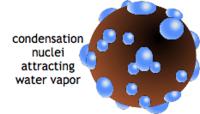
As warm air rises and expands it begins to cool. As it cools relative humidity increases because the volume of air is smaller. When the air reaches 100% humidity, water vapor starts to condense into tiny drops around particles of dust, salt, and smoke. These tiny particles are called nuclei or condensation nuclei. These water drops are extremely small and continue to be suspended in the air. Clouds develop as these water droplets bond together.
After a cloud and the air can no longer hold the weight, the Earth gets precipitation in the form of rain, sleet, hail, and snow. The air temperature determines which type of precipitation will occur. Rain falls when the water is above freezing. When water vapor changes to a solid we call that snow. Sleet happens when snow passes through a warm layer of air, melts, and then freezes near the ground. Freezing rain is precipitation that falls as rain, but the air near the surface of the Earth is below freezing so it freezes quite quickly when it hits an object. Hail stones are lumps of ice that form in cumulonimbus clouds where raindrops rise and fall through the cloud collecting water at the bottom of the cloud and then freezing at the top of the cloud, when the hail is heavier than the force of the turbulent wind can support its weight, gravity pulls it to the surface.
|
|
|
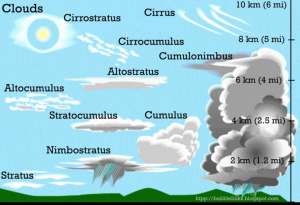
Understanding the types of clouds can help you forecast the weather. Cloud types are based on height, shape, and the amount of moisture contained in them. Prefixes are added to cloud names to distinguish their height. Cirro clouds are very high in the atmosphere. Alto is used when clouds are at middle elevations. Other prefixes like strato mean flat and nimbo refers to rain clouds and cumulo means heap or accumulation.
Below are descriptions of the different cloud types.
Cumulus clouds are puffy white clouds with white flat bases used to play the shape game. Sometimes these clouds are called cauliflower clouds. Cumulus clouds form as warm air columns rise. These types of clouds can indicate that both fair weather is here or that stormy weather is on its way.
Cirrus clouds are those fibrous or curly clouds that look like jet trails. These for high in the atmosphere. They tend to be thin, white, and feathery. Due to their height in the atmosphere, they are made out of tiny ice crystals. Cirrus clouds usually indicate fair weather is on its way and that a warm front is approaching. The word cirrus means tendril or hairlike filament.
Cirrostratus clouds look like very thin veils and are made out of ice crystals that form halos around the moon or sun. These high altitude clouds can indicate both fair weather or an approaching storm.
Cirrocumulus clouds are very high-altitude cumulus clouds. These can appear gray. Sometimes they can take on the appearance of fish scales. If you see cirrocumulus clouds you are probably in for some fair weather, but the temperatures most likely will be cold, as these clouds are most often found during the winter time.
Altostratus clouds are mid-level clouds that look like thick veils with a bluish or grayish tint to them. They are going to be flat long clouds and indicate light continuous precipitation.
Altocumulus clouds are fair-weather clouds. They are similar to cumulus clouds but higher up in the atmosphere, forming cotton ball shapes. They are made from a mixture of ice and water and can sometimes appear slightly gray.
Nimbus clouds are going to be those dark angry-looking clouds. These clouds are associated with precipitation and are full of water. An easy way to tell a nimbus cloud is that light does not penetrate through the cloud.
Stratocumulus clouds are clouds that form groups of cumulus clouds. They will have flattened bottoms and can represent light precipitation.
Cumulonimbus clouds are those huge tall thunderheads. These clouds can start low and grow up to 18,000 meters. If you see cumulonimbus clouds you can be sure that underneath them there is a potential thunderstorm brewing.
Nimbostratus clouds are those clouds that can have streaks that extend to the ground and are full of water, usually precipitating. Lightning or thunder would not usually be present in these clouds. These clouds are low in altitude.
Now that you are professional cloud identifiers, complete the next activity.
If you are a student at Snowflake, Holbrook, or Heber access the assignment from this link. SUSD5 Version of the Cloud Identification Lab
Purchase the Cloud Identification Lab at Teachers Pay Teachers for $0.60 cents.