Daily Dose of Dinos: Are the dinosaurs you know, really dinosaurs?
To begin this chapter, you are going to get to examine different fossils and try to identify them based on certain characteristics that your samples have.
SUSD5 Student Version of the Fossil Identification Lab.
Purchase the Fossil Identification Lab for $0.60 cents at Teachers Pay Teachers. or the Google Doc version for 0.75 cents at Teachers Pay Teachers
Section 1: Fossil Formation
Fossils are the remains, imprints, or traces of once-living organisms that have been preserved in the rock record. Fossils can tell us when (relative time), where (the type of environments), and how they lived. Most prehistoric animal traces do not survive because of decay, scavengers, plate movements, subduction, volcanic eruptions, weathering, etc...
Fossils let scientists understand ancient environments. Rocks have been discovered in Antarctica that contains fossils of tropical plants. Brachiopods lived in shallow seas but are found in the Midwest. Fossils help us understand the historical geology of rock layers that have been found. Fossils help us understand and collect information about ancient environments, climates, and organism behavior, and we even use them to relatively date rocks.
It is extremely difficult to become a fossil. Watch the video below and see how difficult it is.
Conditions that are needed to become fossils are:
- The organism must be protected from scavengers and microorganisms.
- The organism needs to be buried quickly by oxygen-poor sediment.
- Organisms need hard parts like teeth, shells, and bones. If they don't decay, it is most likely going to destroy them.
Fossils are usually found in sedimentary rocks. Think back to what a sedimentary rock is and ask yourself, "Why are fossils most likely found in sedimentary rock?"
Section 2: Types of Fossils
Daily Dose of Dino: Super Predator Discovered in Utah, The King of Gore
There are 5 types of fossils.
Permineralization and Replacement
- Petrified remains are hard and rocklike. The organism's remains have been replaced by mineralization.
- Example: Water dissolves the calcium in bone and then replaces it with the mineral quartz.
- Petrified Wood in the Petrified National Forest is a great example of permineralized fossils.
|
|
|
|
Carbonaceous Films
- Most organism tissue is made of carbon compounds. Sometimes this carbon gets pressed out of the organism caused by a buildup of heat and pressure from overlying sediments. Gases and liquids are forced out of the organism leaving the outline of the carbon residue through a process called carbonization which chemically changes organic material. Think of carbonaceous films like a printing press or photocopy. Nothing is left of the original organism except its filmed copy.
|
|
|
|
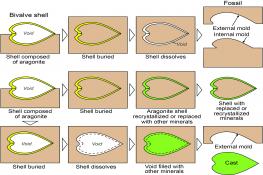
Molds and Casts
- Think of molds and casts like Plaster of Paris impressions. Hard parts of an organism fall into soft sediment like mud from silts and clays. Compaction and cementation turn these sediments into rock. Even though it is rock, it is still porous and permeable allowing water and air to reach the organism causing it to decay inside of the rock. This leaves a hollow spot or a mold. If sediment enters the mold and fills it in a cast fossil is formed.
|
|
|
|
This video will demonstrate how mold and casts are formed.
Original remains
- Sometimes the remains of a complete organism are found.
- Examples: Amber trapping insects, woolly mammoths are frozen. Animals trapped in tar.
- In order to be classified as a fossil, the organism must be at least 10,000 years old. So even though a man that had died 5300 years ago and was recently found in a glacier in the Alps, he would not be considered a fossil.
|
|
|
|
Watch this video to see some awesome facts about the wooly mammoth.
Trace Fossils
- Trace fossils are traces, tracks, and other evidence of ancient life. We can use trace fossils to help determine the sizes and weights of organisms. We can use these fossils to discover possible diets.
- Examples of trace fossils:
- Wormholes, burrows, footprints, eggs, fossilized poop called coprolite, etc...
|
|
|
|